What pmsims does
pmsims estimates the minimum sample size needed to develop a prediction model to achieve a target level of performance with assurance. Rather than relying on simple rules of thumb or closed‑form formulae, pmsims uses simulation to:
- Generate synthetic datasets that reflect your target setting (outcome type, prevalence or \(R^2\), signal vs. noise predictors);
- Fit a specified model (e.g., logistic regression or linear regression);
- Evaluate a chosen performance metric (e.g., calibration slope, AUC); and
- Trace a learning curve of performance as the training size increases.
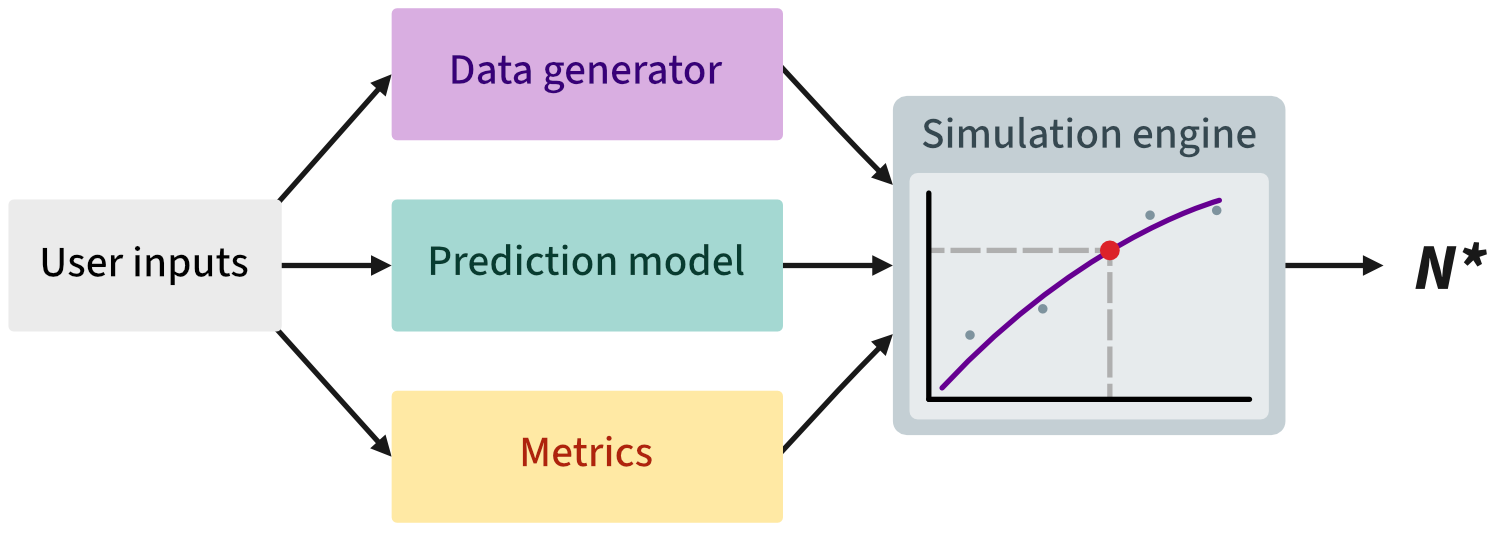
The recommended design objective is assurance: the smallest \(n\) such that a high proportion of repeated studies (e.g., 80%) meet the target performance. In pmsims, this is implemented via the 20th percentile of the simulated performance distribution at each \(n\).
Required inputs at a glance
There are three wrapper functions for binary, continuous, and survival outcomes, respectively:
All three functions share the same basic structure. The table below lists the key inputs.
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
signal_parameters |
(int) Number of true signal predictors associated with the outcome. |
noise_parameters |
(int) Number of noise predictors unrelated to the outcome. |
predictor_type |
(chr) Type of simulated predictors ("continuous" or "binary").
|
binary_predictor_prevalence |
(num 0–1) Prevalence for binary predictors (used only if predictor_type = "binary").
|
outcome_prevalence |
(num 0–1) Target prevalence of the binary outcome. |
large_sample_cstatistic |
(num 0–1) Expected C-statistic for a very large training sample. |
large_sample_rsquared |
(num 0–1) Expected R2 for a very large training sample. |
large_sample_cindex |
(num 0–1) Expected concordance index for a very large training sample. |
model |
(chr) Model used for fitting (e.g. logistic, linear, or Cox). |
metric |
(chr) Performance metric used to estimate the minimum required sample size (e.g. calibration slope, R2, C-statistic). |
minimum_acceptable_performance |
(num) Minimum acceptable performance in the units of the chosen metric (e.g. calibration slope ≥ 0.9). |
n_reps_total |
(int) Total number of simulation replications. |
mean_or_assurance |
(chr) Criterion for summarising results; "assurance" recommended.
|
Notes:
- The engine automatically tunes the data generator so the chosen model reaches the specified large‑sample performance (C‑statistic or \(R^2\)) on very large samples.
- For reproducibility, set a random seed (
set.seed()).
Binary-outcome example
We target the smallest n that meets the assurance criterion.
set.seed(123)
binary_example <- simulate_binary(
signal_parameters = 20,
noise_parameters = 0,
predictor_type = "continuous",
binary_predictor_prevalence = NULL,
outcome_prevalence = 0.30,
large_sample_cstatistic = 0.80,
model = "glm",
metric = "calibration_slope",
minimum_acceptable_performance = 0.85,
n_reps_total = 1000,
mean_or_assurance = "assurance"
)
binary_example#> ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐
#> │ pmsims: Sample size simulation summary │
#> └────────────────────────────────────────┘
#> ──────────────────────────────────── Inputs ────────────────────────────────────
#> Outcome : binary
#> Predictor type : continuous
#> Number of predictors : 20
#> Noise predictors : 0
#> Prevalence : 0.3
#> Expected large-sample performance : C-statistic ('cstatistic') = 0.800
#> Target for chosen performance metric : Calibration slope ('calib_slope') = 0.850
#> Model : glm
#> Simulation reps : 1,000
#> ──────────────────────────────────── Results ───────────────────────────────────
#> Final minimum sample size : 1,173
#> Estimated performance at N : 0.849 (Calibration slope ('calib_slope') = 0.850)
#> Model : glm
#> Mode : Assurance
#> Running time : 1 minute
#> Assurance mode ensures the target metric is met with high probability across repeated datasets.Plot the estimated learning curve and identified sample size:
plot(binary_example)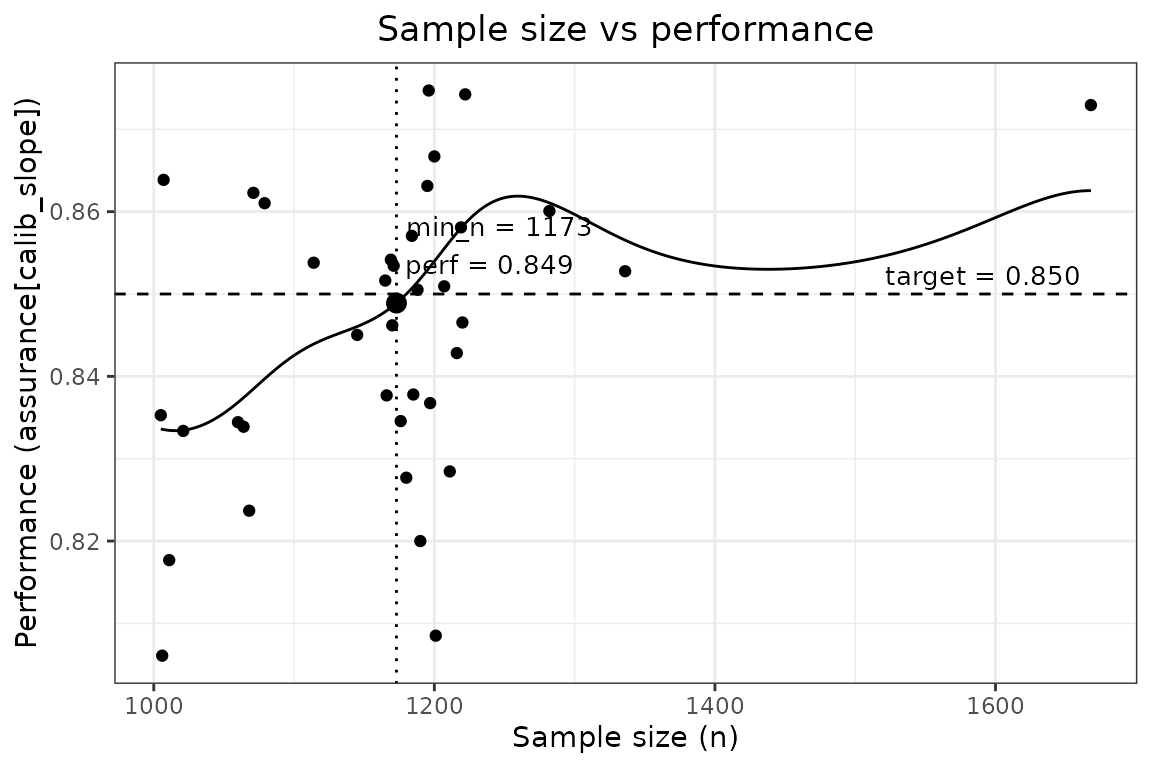
Continuous-outcome example
continuous_example <- simulate_continuous(
signal_parameters = 15,
noise_parameters = 0,
predictor_type = "continuous",
large_sample_rsquared = 0.50,
model = "lm",
metric = "calibration_slope",
minimum_acceptable_performance = 0.90,
n_reps_total = 1000,
mean_or_assurance = "assurance"
)
continuous_example#> ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐
#> │ pmsims: Sample size simulation summary │
#> └────────────────────────────────────────┘
#> ──────────────────────────────────── Inputs ────────────────────────────────────
#> Outcome : continuous
#> Predictor type : continuous
#> Number of predictors : 15
#> Noise predictors : 0
#> Expected large-sample performance : R² ('r2') = 0.500
#> Target for chosen performance metric : Calibration slope ('calib_slope') = 0.900
#> Model : lm
#> Simulation reps : 1,000
#> ──────────────────────────────────── Results ───────────────────────────────────
#> Final minimum sample size : 271
#> Estimated performance at N : 0.899 (Calibration slope ('calib_slope') = 0.900)
#> Model : lm
#> Mode : Assurance
#> Running time : 14 seconds
#> Assurance mode ensures the target metric is met with high probability across repeated datasets.
plot(continuous_example)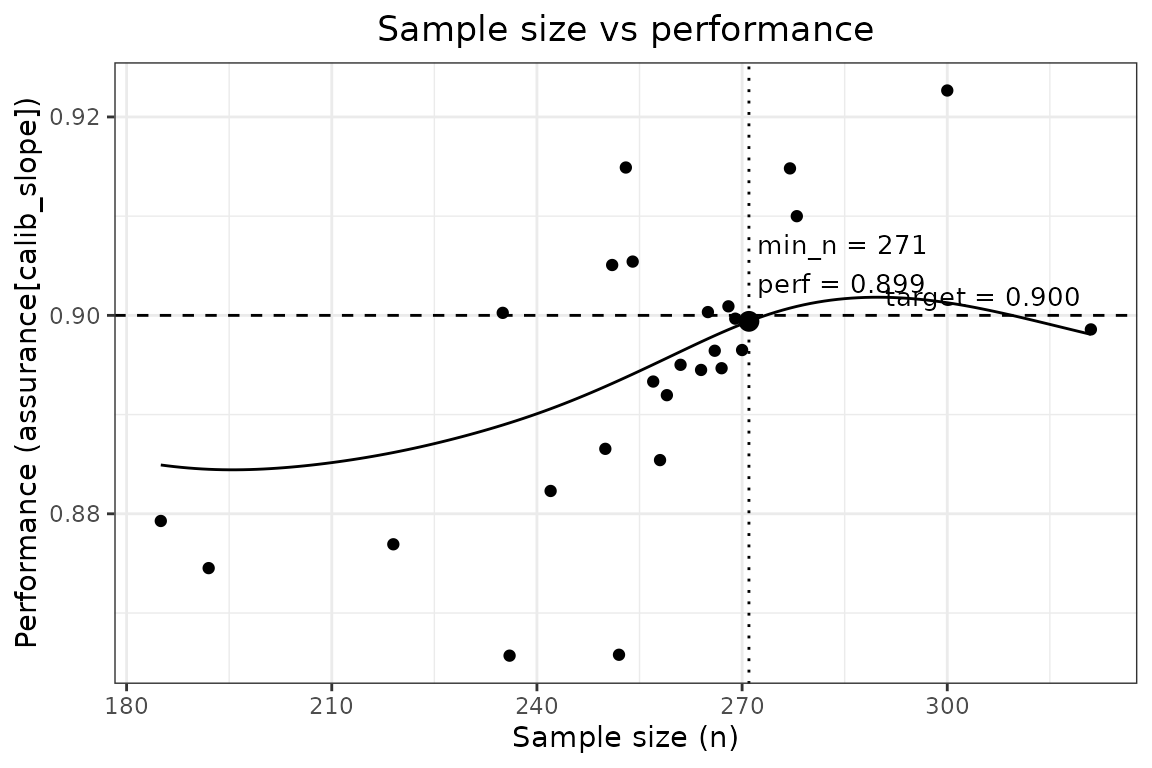
Session info
sessionInfo()
#> R version 4.5.2 (2025-10-31)
#> Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
#> Running under: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS
#>
#> Matrix products: default
#> BLAS: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libblas.so.3
#> LAPACK: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libopenblasp-r0.3.26.so; LAPACK version 3.12.0
#>
#> locale:
#> [1] LC_CTYPE=C.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C LC_TIME=C.UTF-8
#> [4] LC_COLLATE=C.UTF-8 LC_MONETARY=C.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=C.UTF-8
#> [7] LC_PAPER=C.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C LC_ADDRESS=C
#> [10] LC_TELEPHONE=C LC_MEASUREMENT=C.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
#>
#> time zone: UTC
#> tzcode source: system (glibc)
#>
#> attached base packages:
#> [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
#>
#> other attached packages:
#> [1] pmsims_0.5.0
#>
#> loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
#> [1] Matrix_1.7-4 gtable_0.3.6 jsonlite_2.0.0 compiler_4.5.2
#> [5] crayon_1.5.3 jquerylib_0.1.4 splines_4.5.2 systemfonts_1.3.1
#> [9] scales_1.4.0 textshaping_1.0.4 yaml_2.3.10 fastmap_1.2.0
#> [13] lattice_0.22-7 ggplot2_4.0.0 R6_2.6.1 labeling_0.4.3
#> [17] knitr_1.50 htmlwidgets_1.6.4 desc_1.4.3 bslib_0.9.0
#> [21] RColorBrewer_1.1-3 rlang_1.1.6 cachem_1.1.0 xfun_0.54
#> [25] fs_1.6.6 DiceKriging_1.6.1 sass_0.4.10 S7_0.2.0
#> [29] cli_3.6.5 pkgdown_2.2.0 withr_3.0.2 digest_0.6.37
#> [33] grid_4.5.2 lifecycle_1.0.4 mlpwr_1.1.1 vctrs_0.6.5
#> [37] evaluate_1.0.5 glue_1.8.0 farver_2.1.2 ragg_1.5.0
#> [41] survival_3.8-3 rmarkdown_2.30 tools_4.5.2 htmltools_0.5.8.1